
If you read Node.js's definition, it mentions an event-driven architecture and its ability to handle asynchronous I/O. These two concepts are crucial to understand, so take your time to read and grasp them thoroughly. We know JavaScript is a synchronous, single-threaded language, meaning the code runs in one direction like a one-way road, with one task executing at a time. JavaScript code executes line by line, which is what makes it synchronous and single-threaded.

Synchronous vs Asynchronous Code
Imagine a restaurant where you can get Coke, pizza, and noodles, which take 0 minutes, 10 minutes, and 5 minutes to prepare, respectively. Now, picture a line of 5 people (A, B, C, D, E) waiting to order. In a synchronous way, Person A orders Coke and gets it instantly. Person B orders noodles, taking 5 minutes. Person C, who wants pizza, has to wait 5 minutes before even placing the order, then waits another 10 minutes for the pizza. Meanwhile, Person D, who only wants a Coke, ends up waiting unnecessarily. This is how synchronous code works: one task at a time, causing delays.
Asynchronous Way of Running Things
In an asynchronous way, tasks that take time (like preparing pizza or noodles) are handled separately, allowing the restaurant to serve quick orders (like Coke) immediately. So, A gets Coke instantly, while B and C (who ordered pizza and noodles) are moved to a different queue to wait. Meanwhile, D, who also wants Coke, gets served right away. This prevents unnecessary waiting. The completion of B and C's orders depends on the preparation time. Asynchronous operations in Node.js prevent blocking, improving efficiency, especially for quick tasks. JS Engines loves synchronous code because it can run that code in milliseconds. we will see some examples soon.
How synchronous code runs in the JS engine?
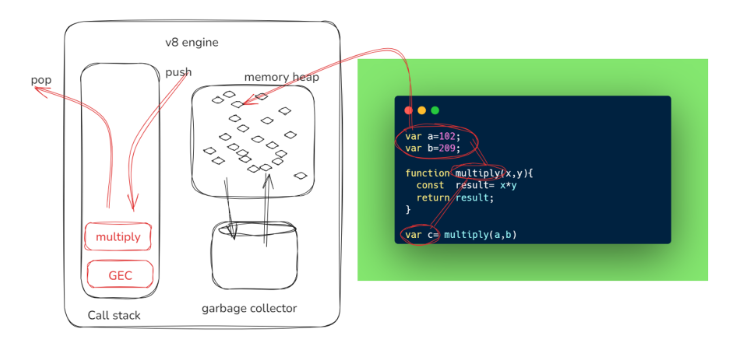
The JS engine has components like the Call Stack, Garbage Collector, and Memory Heap. These aren't machines or hardware; they are just C++ code. When you run a code like var a = 10;, it executes in the Global Execution Context, which is created in a synchronous, single-threaded manner. When a function is called, a new execution context is created for that function, and the code runs. Let me give you an example to explain it further.
var a=102;
var b=209;
function multiply(x,y){
const result= x*y
return result;
}
var c= multiply(a,b)
When the JS engine executes code, it goes through several steps, such as parsing and tokenization. The compiler and scope work together during this phase. For example, when the compiler sees variables a and b, it checks with the scope if they exist. If not, they are declared and assigned values. This process occurs in the Global Execution Context within the Call Stack. When a function is called, a new execution context is created, runs, and then is popped off the stack. For more details, you can learn from blogs or videos by Akshay Saini on YouTube.
How Asynchronous Code Runs in the JS Engine

Let me tell you something: JavaScript isn't just limited to running code. As a scripting language, it has many tasks it's not inherently capable of handling, such as interacting with the outside world, accessing files, or databases. A great example is managing time with setTimeout—this isn't actually a feature of JavaScript itself. Really? Yes! The JS engine can't inherently wait; it's not designed for that. The JS engine's responsibility is simply to take JavaScript code and convert it, that's it—no time management or other logic involved.
That's where Node.js comes into play with its superpowers. Node.js can execute timers, read files from the OS, access databases, connect to servers, and make internet requests. When all these operations are ready, only the JavaScript code runs on the V8 engine. These superpowers are managed by and connected to the V8 engine through libuv. Yes, my friend, libuv! Whenever a request for file access, an internet call, or a timer comes in, it goes to libuv, which communicates with the OS and then gets back to the V8 engine. And work is done by Js v8 engine in the callstack.
In simple terms, this is how Node.js operates.
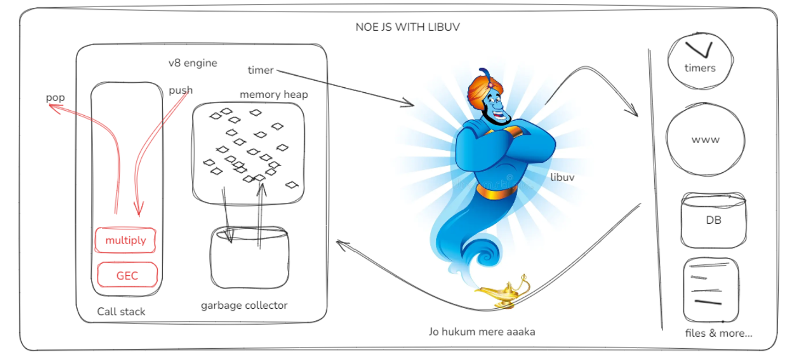
What is libuv the Superhero
libuv is a C library that provides Node.js with an event-driven, asynchronous I/O model. It helps manage tasks like file reading, writing, networking, and timers in a non-blocking way, making it possible for Node.js to handle many tasks simultaneously without slowing down. Essentially, Libuv is what enables Node.js to be fast and efficient, handling multiple operations at once without waiting for each to finish. Libuv acts as a middleware b/w JS engine and Operating System. Libuv has thread pool and event loop will discuss in later blogs. just know if anything comes async or engine can’t handle it ask libuv to do it. find the libuv exact link to check the code of it written in c for your reference. actually libuv does so many things.
Node.js is Asynchronous
If someone asks about Node.js behavior, tell them Node.js is overall asynchronous. However, V8, which is its JavaScript engine, operates synchronously. Node.js gains its asynchronous nature from superpowers like libuv, which enables non-blocking I/O operations. This is why Node.js is known for its non-blocking behavior, allowing I/O operations to be performed asynchronously. And don't forget to give a shoutout to the creator of Node.js, Ryan Dahl!
And that's all for this episode!
I'm Ashutosh Anand Tiwari, and I'm writing digital notes on Node.js. If you enjoy these notes, please share them with your friends. If you find any errors or have improvements, feel free to contribute by visiting this link. If you're interested in writing the next episode's notes, visit this link. Let's learn together! Also, please consider giving a star to this repo. For any queries, let's connect here.
New words to search
- IO
- Async and sync
- Garbage collector
- Libuv
Questions / Queries to research
- Read the C code of libuv
- How garbage collector works in JavaScript ?
- Find the code of Garbage collector in Node Js github repo.
Useful Tips
- Node Js is asynchronousd and Js engine in syncronous,
Useful links

Thank you so much for reading. If you found it valuable, consider subscribing for more such content every week. If you have any questions or suggestions, please email me your comments or feel free to improve it.

Written by Rahul Aher
I'm Rahul, Sr. Software Engineer (SDE II) and passionate content creator. Sharing my expertise in software development to assist learners.
More about me