Remove Duplicates

Remove Duplicates
Problem Statement:
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same. Then return the number of unique elements in nums.
Consider the number of unique elements of nums to be k. To get accepted, you need to do the following things:
Change the array nums such that the first k elements of nums contain the unique elements in the order they were present in nums initially. The remaining elements of nums are not important, as well as the size of nums. eturn k.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output: 2, nums = [1,2,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively. It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
Constraints:
1 ≤ nums.length ≤ 3 * 104
-100 ≤ nums[i] ≤ 100
nums is sorted in non-decreasing order.
Important Points:
Non-decreasing order: The array is sorted such that elements can stay the same or increase: nums[i] <= nums[i+1].
Examples:
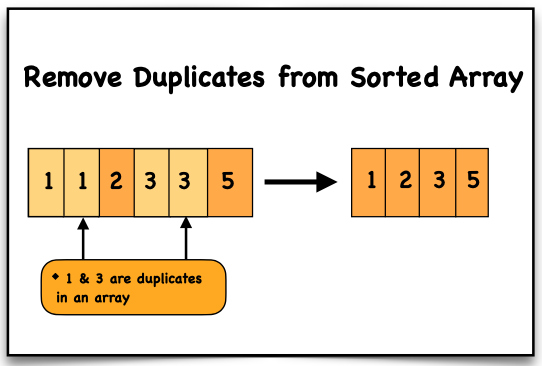
Valid: [1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 5]
Invalid: [3, 2, 1] (this is decreasing).
In-place:
You must modify the given nums array itself. You are not allowed to use extra arrays for storing the result.
Approach:
x = 0:Pointer to track the last unique element's position.- Loop through the array from
i = 0tonums.length. - If true (new unique value), increment
xand updatenums[x] = nums[i]. - This shifts the unique value forward in the array.
- At the end,
x + 1gives the count of unique elements.
Time Complexity:
- The function uses a single loop that iterates through the entire array once.
Each iteration performs constant-time operations (comparisons and assignments).
Time Complexity = O(n), wheren = nums.length.
Space Complexity:
- The function modifies the array in-place.
Uses only a few extra variables:xandi.
Space Complexity = O(1)(constant extra space).
Dry Run
Input: [1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 5]
Initial state:
x = 0
i = 0: nums[i] = 1, nums[x] = 1 → NOT greater → skip
i = 1: nums[i] = 1, nums[x] = 1 → NOT greater → skip
i = 2: nums[i] = 2, nums[x] = 1 → GREATER → x=1, nums[1] = 2
i = 3: nums[i] = 3, nums[x] = 2 → GREATER → x=2, nums[2] = 3
i = 4: nums[i] = 3, nums[x] = 3 → NOT greater → skip
i = 5: nums[i] = 5, nums[x] = 3 → GREATER → x=3, nums[3] = 5
Final array: [1, 2, 3, 5, 3, 5]
Unique count: x + 1 = 4
Output: 4 (First 4 elements are unique: [1, 2, 3, 5])
Visualisation:
JavaScript Code
var removeDuplicates = function(nums) {
let x = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[x]) {
x++;
nums[x] = nums[i];
}
}
return x + 1;
};
Edge Cases to Consider:
1. Single Element Array:
- Input: nums = 1
- Output: 1 (only one unique element)
2. All Same Elements:
- Input: nums = 5, 5, 5, 5
- Output: 1 (only one unique element: 5)
3. All Different Elements:
- Input: nums = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- Output: 5 (all elements are unique)
4. Two Elements - Same:
- Input: nums = 1, 1
- Output: 1
5. Two Elements - Different:
- Input: nums = 1, 2
- Output: 2
6. Negative Numbers:
- Input: nums = -3, -3, -2, -1
- Output: 3
7. Large Array:
- Arrays up to 3 × 10^4 elements should be handled efficiently.
Key Takeaways:
- Two-pointer technique is efficient for in-place array modifications.
- Sorted array property: Duplicates are adjacent, making detection simple.
- In-place modification saves space - O(1) extra space vs O(N) for creating new array.
- Pointer x tracks position: x always points to the last unique element's position.
- Order preservation: Relative order of unique elements is maintained.
- Applications:
- Data deduplication
- Preprocessing for algorithms requiring unique elements
- Memory optimization in sorted collections
- Interview strategy:
- Explain the two-pointer approach clearly.
- Walk through with an example.
- Mention that array must be sorted.
- Discuss in-place modification benefit.
- Common mistakes:
- Not handling empty arrays.
- Comparing wrong elements (should compare with last unique, not previous).
- Forgetting to return x + 1 (count, not index).
- Related problems:
- Remove duplicates allowing at most k occurrences.
- Remove duplicates from unsorted array.
- Find duplicates in array.
- Performance: O(N) time with O(1) space is optimal for this problem.

Written by Rahul Aher
I'm Rahul, Sr. Software Engineer (SDE II) and passionate content creator. Sharing my expertise in software development to assist learners.
More about me